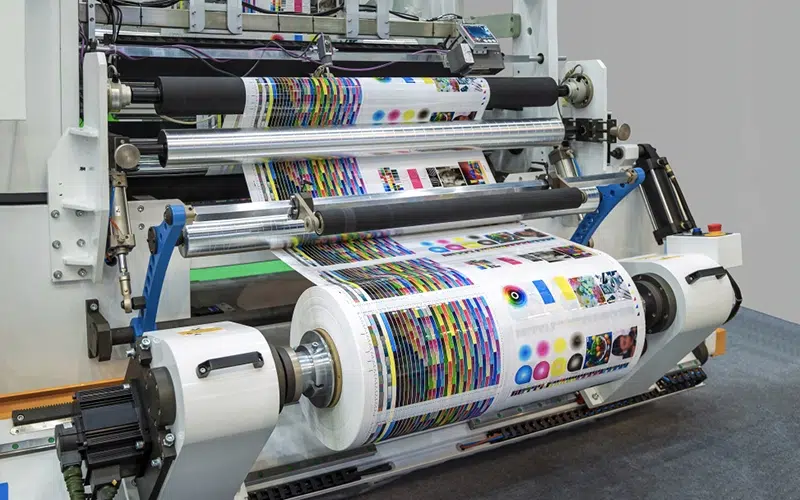
Developing the perfect packaging solution requires understanding the various printing methods available in today’s market. The packaging printing method you choose will determine not only the visual appeal but also the durability and eco-friendliness of your final product. Here is our compilation of seven common packaging printing processes.
1. Flexographic Printing
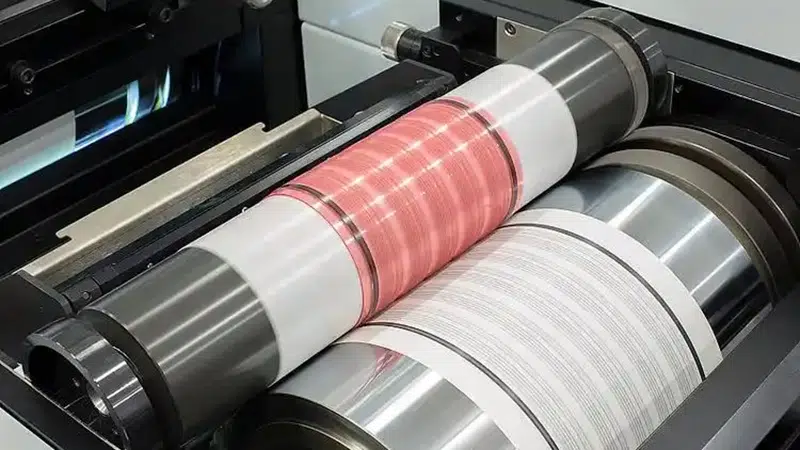

Flexographic printing is a rotary printing method commonly used for printing corrugated cardboard, plastic bags, labels, and films for packaging materials. It offers high speed and is suitable for long-run printing on various substrates.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient for large volume production runs
- Compatible with a wide range of substrates, including flexible materials
- Relatively low cost per unit
- Environmentally friendly with water-based and UV inks options
- Quick setup and changeover times compared to some other methods
- Good durability and resistance to environmental factors
Disadvantages:
- Typically lower print quality compared to offset printing, though this gap has narrowed with technological advancements
- Requires the creation of printing plates or sleeves
- Limited ability to reproduce fine details and subtle gradients
- Color consistency can be challenging to maintain throughout long runs
2. Offset Printing

Offset printing is commonly used for cardboard box packaging and books. It can produce high-quality printed products in large quantities, making it ideal for packaging with complex content. It remains one of the most popular printing methods today.
Advantages:
- Excellent print quality, particularly suitable for packaging with complex graphics
- Ideal for large-scale mass production
- Consistent high-quality image reproduction
- Capable of printing fine details and smooth color gradients
- Cost-effective for medium to large print runs
- Wide range of color options and special finishes available
Disadvantages:
- Higher costs for small production runs
- Requires significant preparation time before production begins
- Not ideal for variable data printing
- Less environmentally friendly due to chemical processes involved
- Requires regular maintenance and skilled operators
3. Gravure Printing
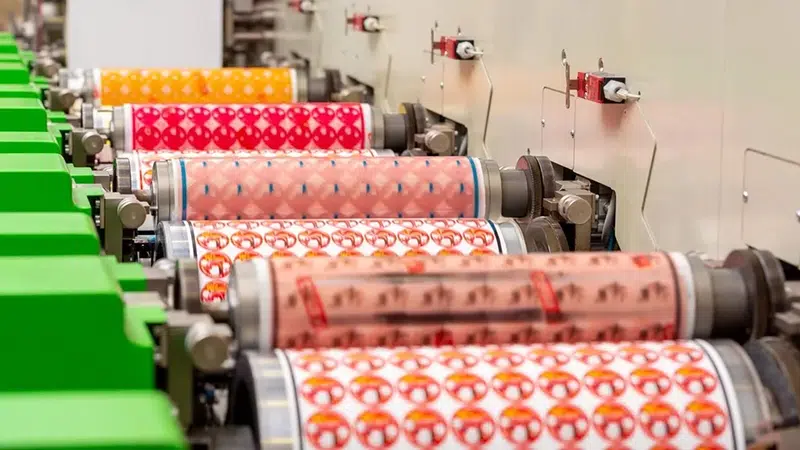

Gravure printing is an engraved printing process used for high-quality packaging such as flexible packaging, labels, and plastic films. It can reproduce highly detailed images but is expensive.
Advantages:
- High print quality with excellent detail reproduction
- Suitable for long-term use and extended print runs
- Consistent color reproduction throughout the print run
- Excellent for metallic inks and special effects
- Durable prints with good resistance to fading
- Capable of printing on thin films and flexible materials
Disadvantages:
- High cost, especially for small production runs
- Complex process requiring the production of engraved cylinders
- Long setup times and high initial investment
- Less environmentally friendly due to solvent-based inks
- Limited flexibility for design changes once cylinders are created
4. Screen Printing
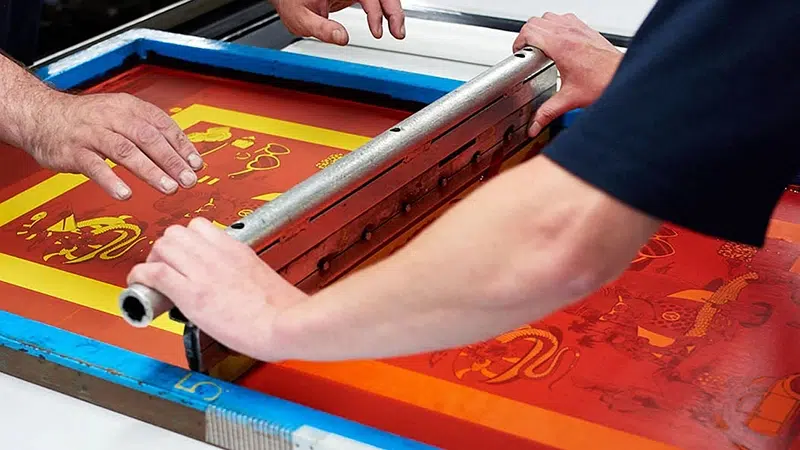

Screen printing can be applied to various materials including paper, cardboard, wood, metal, textiles, and more. Beyond industrial printing, screen printing is widely used in textile dyeing, clothing, signage, radio and electronics, ceramics, and packaging industries.
Advantages:
- Low plate-making costs
- Simple and convenient equipment operation with flexible production and minimal quantity requirements
- Wide range of printable substrates
- Produces thick, textured ink layers with a tactile quality
- Rich in expressive possibilities with diverse printing materials
- Ability to print specialty inks, metallic colors, and glow-in-the-dark effects
- Can print on irregular surfaces and three-dimensional objects
Disadvantages:
- More suitable for single-color printing; registration accuracy is low, making multi-color printing challenging
- Not ideal for full-color work; relatively lower precision and less refined gradations
- Not suitable for gradient color printing
- Slower production speeds compared to other methods
- Requires significant drying time and space
- Limited resolution for very fine details
5. Digital Printing
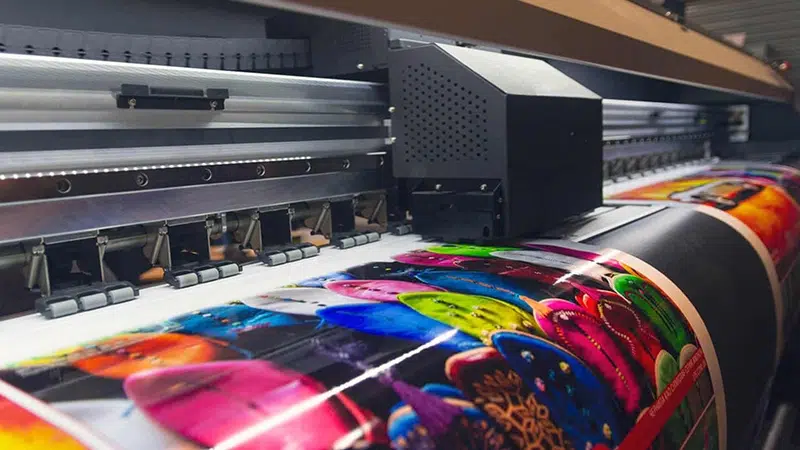

Digital printing is increasingly used for customized packaging or small-batch printing. It offers tremendous flexibility for customization, allowing quick job changes without requiring printing plates.
Advantages:
- Exceptional flexibility for small batches and customization
- No printing plates required, reducing setup time and costs
- Ability to print variable data and personalized packaging
- Quick turnaround times for short runs
- Minimal waste during setup
- Easy to make last-minute design changes
- Cost-effective for prototyping and sample production
Disadvantages:
- Higher costs compared to traditional methods for large production runs
- Print quality may be limited compared to other methods, particularly for certain color ranges
- Size limitations depending on the equipment
- Less durable in some applications compared to traditional printing methods
- Limited substrate options compared to conventional printing
- Color consistency can vary between print runs
6. Letterpress Printing

Letterpress printing is an ancient printing method that has largely been replaced by more modern technologies. However, it is sometimes used for printing special patterns on luxury packaging or creating artistic effects.
Advantages:
- Suitable for small-scale runs
- Creates a unique raised printing effect with tactile quality
- Delivers a premium, crafted appearance highly valued in luxury packaging
- Creates distinctive impressions that convey quality and tradition
- Ideal for embossing and specialty finishes
- Appeals to consumers seeking artisanal or handcrafted aesthetics
Disadvantages:
- Less common and less efficient compared to other modern methods
- Limited in quality and complexity of designs
- Requires specialized equipment and skilled craftspeople
- Time-consuming setup and production process
- Higher labor costs than automated printing methods
- Limited color options in a single pass
7. Inkjet Printing
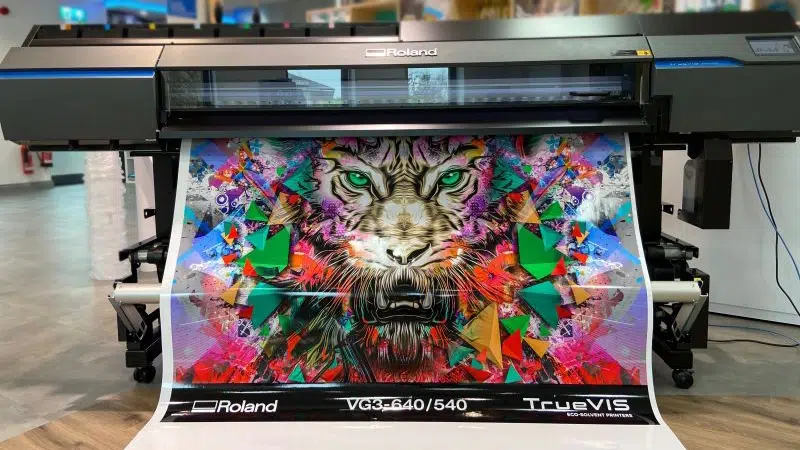

Inkjet printing is a complementary printing technology. It’s fast and suitable for customized and small-batch packaging, commonly used for printing barcodes, expiration dates, and other variable information.
Advantages:
- Great flexibility for customization and variable data
- Relatively low cost for small-batch production
- No plate making required, enabling on-demand printing
- Capable of printing on various shapes and materials
- Minimal setup time and waste
- High-resolution capabilities with newer systems
- Good for adding variable information to pre-printed packaging
Disadvantages:
- Print quality may be limited compared to other methods
- Lower printing speed for large-volume production
- Less durable prints that may fade or smudge without proper coating
- Higher ink costs compared to traditional printing methods
- May require special surface treatments for certain substrates
- Limited color gamut compared to some traditional methods
Ready to elevate your product presentation? As a sustainable packaging solution provider, GVPAK offers comprehensive custom packaging solutions designed to make your products stand out in today’s competitive marketplace. Contact GVPAK today to create packaging that impresses your customers and respects our planet.