Basic Design Standards for Molded Pulp
The following standards are established for regular production requirements to ensure consistent quality, structural integrity, and efficient manufacturing processes for molded pulp products.
1. Corner Radius
Standard: Radius ≥ 12mm
Why it matters: Larger radii reduce stress concentrations, improve load-bearing capacity, and prevent cracking during molding. Molds should ensure smooth transitions at corners for better stability.
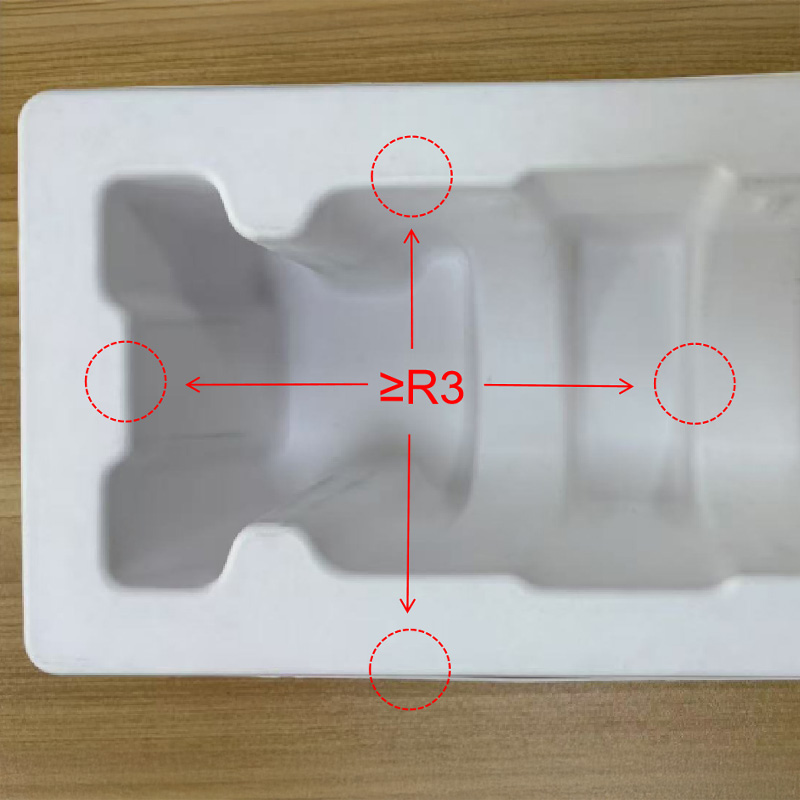
2. Edge Radius
Standard: Radius ≥ 3mm
Why it matters: Rounded edges improve mold release and reduce fiber breakage risks. A minimum radius of 3mm is recommended to prevent weakening of the product's strength due to stress concentrations.
3. Draft Angle
Standard: ≥ 3°
Why it matters: Too small an angle makes demolding difficult and can cause deformation during the transfer of wet blanks. A draft angle of 1-5° is ideal, with 3° required for complex molds to ensure smooth release.
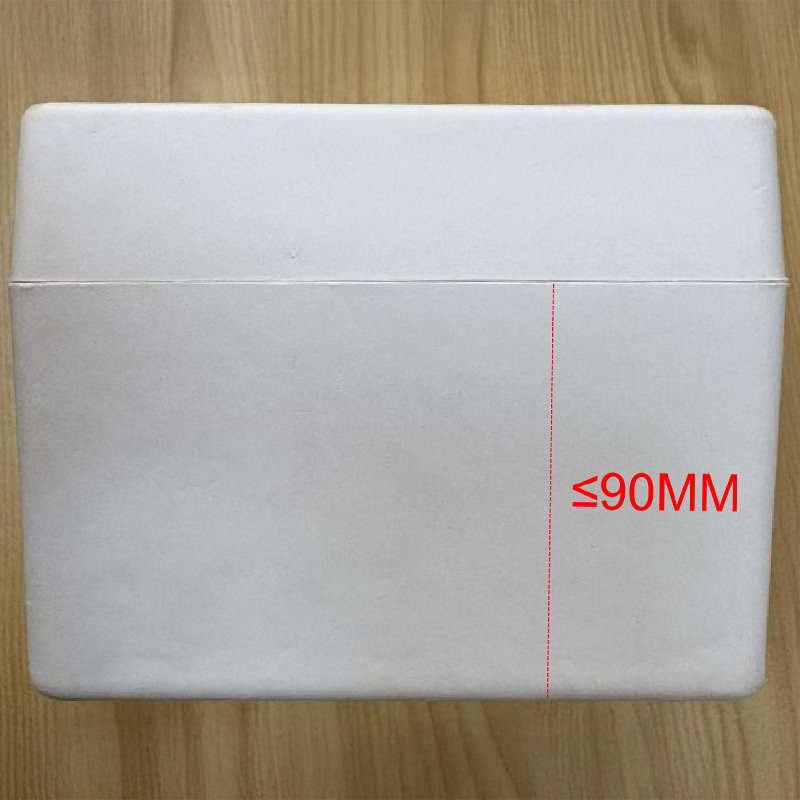
4. Depth Limit
Standard: Single depth ≤ 90mm
Why it matters: Excessive depth decreases load-bearing capacity. Reinforcement ribs can help compensate for this. A height-to-circumference ratio of ≤ 5 is recommended to maintain structural stability.
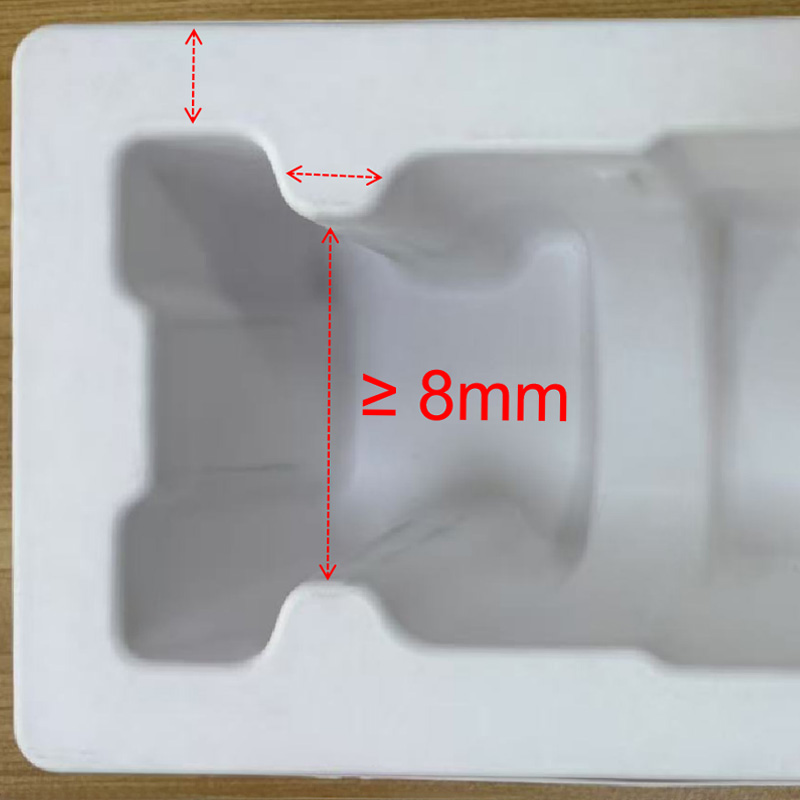
5. Cavity Spacing (Bridging)
Standard: ≥ 8mm
Why it matters: Insufficient spacing can lead to fiber bonding during molding, affecting the structural integrity. Symmetric distribution of ribs and cavities can resolve strength issues in larger cavities.
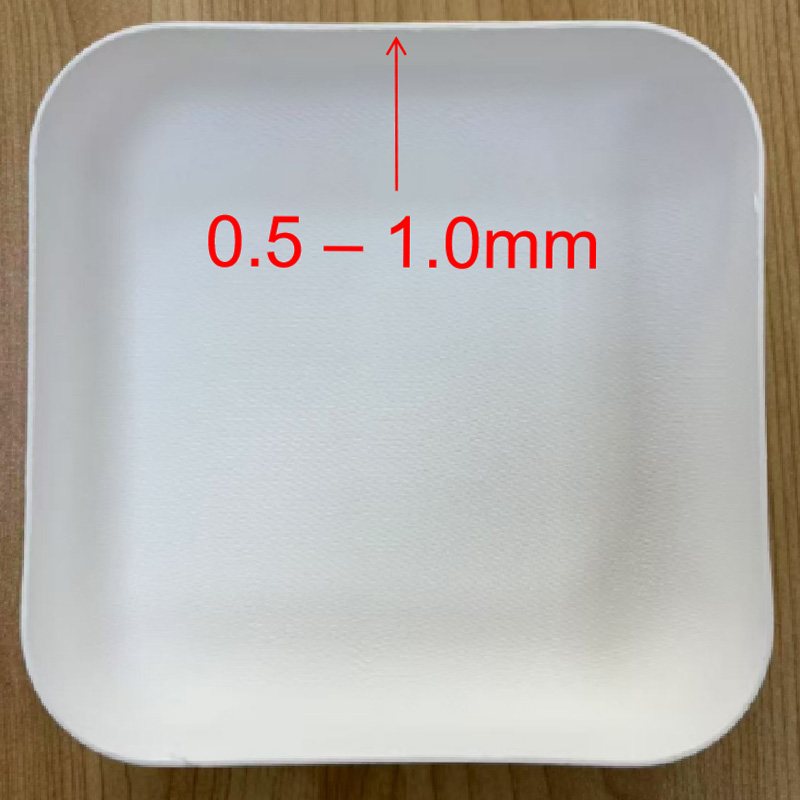
6. Wall Thickness
Standard: 0.5–1.0mm
Why it matters: This range ensures sufficient structural strength while keeping the product lightweight and efficiently moldable. Too thick increases drying time; too thin compromises durability.
Advanced Optimization Solutions
The following advanced techniques may require cost increases and involve yield risks, but offer significant improvements in design possibilities and product performance.
1. Vertical Corner Radius Optimization
Target: Radius ≥ 8mm
How to achieve: Use high-precision aluminum molds (e.g., 6061 aluminum alloy) and wet pressing techniques to reduce fiber resistance at corners.
3. Draft Angle Optimization
Target: 1° (approaching 0° after drying)
How to achieve: Use semi-dry pressing (35% moisture content) combined with mold-injection spraying to compensate for angle using material shrinkage (requires precise shrinkage control, about 3%).
2. Edge Corner Radius Optimization
Target: Radius ≥ 0.5mm
How to achieve: Employ laser-engraved molds and powder metallurgy techniques, controlling edge precision with spray forming technology (additional post-processing required).
4. Cavity Spacing Compression
Target: ≥ 5mm
How to achieve: Optimize the net mold aperture (0.15-0.25mm) and vacuum distribution through micro-channel channels for uniform slurry absorption, enhancing local strength with a dual suction molding process.
Technical Considerations for Implementation
| Parameter |
Standard Value |
Advanced Value |
Cost Impact |
| Corner Radius |
≥ 12mm |
≥ 8mm |
+15-20% |
| Edge Radius |
≥ 3mm |
≥ 0.5mm |
+25-30% |
| Draft Angle |
≥ 3° |
1° |
+15-20% |
| Cavity Spacing |
≥ 8mm |
≥ 5mm |
+35-50% |
When implementing these advanced techniques, several factors must be considered to ensure successful production:
Material Selection
Fiber type, length distribution, and additives significantly impact the ability to achieve advanced specifications. Virgin fibers typically offer better performance than recycled material for precision applications.
Processing Conditions
Temperature, pressure, and dwell time during molding and drying phases must be precisely controlled. Small variations can significantly impact dimensional stability and surface quality.
Equipment Specifications
Advanced mold design requires precision manufacturing equipment. CNC machining with tolerances of ±0.01mm is often necessary for creating molds capable of achieving the optimized specifications.
Future Developments in Molded Pulp Technology
Please note that technology is constantly evolving. If you have any breakthroughs in new technologies or design challenges to discuss, feel free to email us at:
[email protected].
Contact Our Technical Team