In the modern high-speed and highly competitive market, packaging is far more than just a container; it is also a powerful communication tool between customers and manufacturers. Understanding the latest packaging trends will be helpful for brand owners, product designers, and suppliers, whether you operate in food and beverage, cosmetics, electronics, perfume, or other industries. This article focuses on the top packaging design trends for 2026. We’ll unpack what makes these trends popular and how you can apply these ideas.
Biggest New Packaging Trends 2026
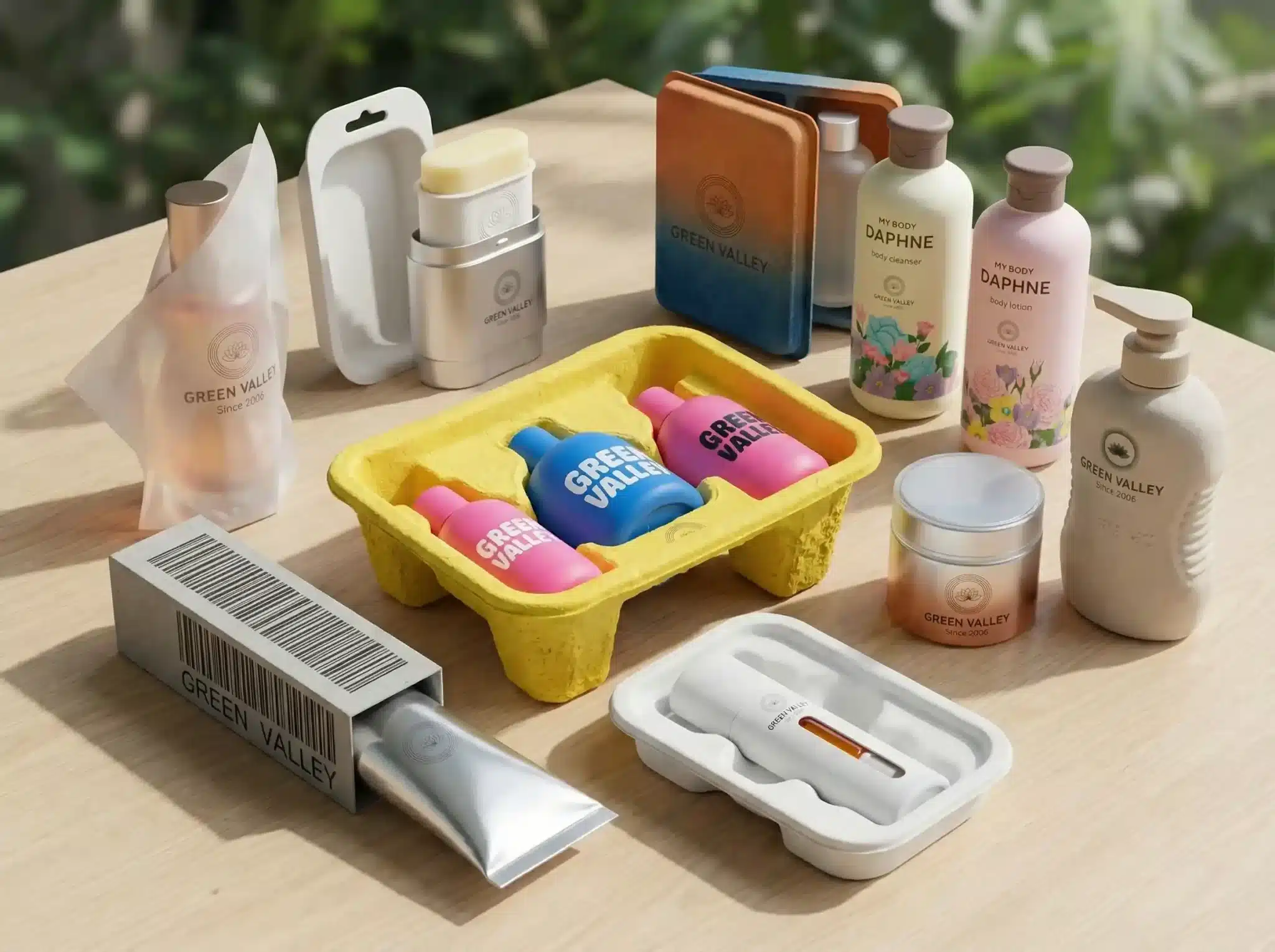
Judging from the overall packaging trends in recent years, intelligentization and sustainability have become the general trend. The application of technology has made people’s lives more convenient, and eco-friendly packaging is constantly improving. Let’s take a look at the biggest packaging industry trends, which mainly involve packaging materials, visuals, and functions.
1. Compliance First
New packaging laws and regulations are shaping the industry in 2026. For example, the Australian Recycling Label (ARL) will become a must-have on product packaging. This label helps customers understand how to recycle the materials properly. Additionally, packaging that uses soft plastics or pouches must no longer include “return to store” messages, as these will be penalized starting next year. Brands will also face new fees based on how much packaging they put on the market, especially if it contains plastics that cannot be recycled. Using recyclable materials or recycled content can reduce these fees, so companies need to pay close attention to these evolving rules to avoid fines and support environmental goals.
Why Are Sustainable and Recyclable Packaging Important?
Sustainable and recyclable packaging is trending because it addresses urgent environmental, social, and economic challenges while meeting growing consumer demand and regulatory requirements. Sustainable packaging uses renewable, biodegradable, or recyclable materials designed to reduce waste, pollution, and carbon emissions. Unlike traditional plastics that can take hundreds of years to decompose, sustainable alternatives like recycled cardboard and biodegradable plastics break down more quickly and lessen landfill dependency.
Moreover, sustainable packaging contributes to social equity and economic resilience. It promotes fair labor practices and community engagement while creating new jobs and stimulating innovation in green materials and logistics. However, the transition comes with challenges, such as supply shortages of recycled plastics and the complexity of sustainability transformations, which only a few companies achieve fully.
Gvpak.com is a professional sustainable packaging company that provides eco-friendly, recyclable, and biodegradable packaging solutions that help combat plastic waste and conserve natural resources. We offer custom packaging options based on your specific needs for various industries.
2. Smart Codes & QR Codes
Traditional barcodes are gradually being replaced by QR codes, which offer much more than just product identification. Consumers can scan these codes with their phones to access detailed information like batch numbers, expiration dates, and even the product’s story or ingredients. This not only helps brands improve transparency but also supports tracking and safety throughout the supply chain. On the other hand, it may also arouse consumers’ curiosity. As printing technology improves, QR codes will become common on packaging worldwide. Europe plans to introduce digital product passports by 2027, which will rely heavily on QR codes.
3. Mono-Material Packaging
Packaging made from a single type of plastic is gaining momentum because it simplifies recycling and production. Many brands are moving away from layered or laminated materials, which are difficult to separate and recycle. Instead, using one kind of plastic, such as polypropylene (PP) or polyethylene (PE) for all parts of the packaging, including caps, bottles, and pumps, makes recycling easier and more efficient, and also reduces waste and supports a circular economy by ensuring that packaging materials can be reused rather than discarded.
What Is Mono-Material Packaging and What Is It Used For?
Mono material packaging refers to the packaging made from a single type of material, such as paper, plastics, glass or metals. The main applications of mono-material packaging is the food sector, which generates a large share of waste. Common examples are PET beverage bottles, glass bottles, cardboard food containers and chip bags. pharmaceuticals and cosmetics also choose this packaging idea for sustainability.
4. Refillable Packaging
Refillable packaging systems are becoming more popular as consumers and brands seek to reduce waste. These systems often use airless pumps or containers that can be refilled multiple times, such as refillable deodorant containers, so the new packaging need can be cut down. This trend also complements mono-material packaging efforts, as simpler materials make refilling and recycling more effective. Refillable packaging helps extend the life of containers and promotes a more sustainable way to enjoy beauty and wellness products.
Main Industries and Examples of Refillable Packaging
- Skincare and cosmetics: Refillable bottles for shampoos and conditioners, cosmetic containers for creams and lotions.
- Household cleaners: Concentrate refills reduce packaging weight and cost.
- Food and Beverage: Reusable jars and caps for dry goods (e.g., spices, instant coffee), refillable beer bottles, milk powder refill packs, aluminum bottles for sparkling water and other drinks
5. PCR Packaging
Using recycled plastic in packaging is no longer just a nice-to-have feature but a growing requirement. Brands are expected to include verified amounts of post-consumer recycled (PCR) content in their plastic packaging. This shift supports reducing reliance on new, virgin plastics and helps close the loop in plastic use. Consumers are becoming more aware and demand greater transparency about what goes into packaging materials. Therefore, it’s important for companies to provide clear, honest information about PCR content to avoid misleading claims and build trust with their customers.
What Does PCR Mean in Packaging?
PCR stands for Post-Consumer Recycled in packaging. PCR packaging is often made from plastics like PET, PP, and HDPE that have been used by consumers, collected after use, cleaned, and reprocessed into new plastic resin. This recycled resin is then used to manufacture new packaging products. Simply put, PCR packaging gives a second life to used plastic materials by turning them back into packaging instead of letting them go to waste.
Benefits of PCR Packaging
Using PCR packaging mainly benefits the environment by reducing reliance on virgin plastics, which are made from fossil fuels and have a high carbon footprint. By recycling plastic waste, PCR packaging helps reduce landfill, ocean pollution, and resource depletion.
6. Lightweight Packaging
Reducing the weight of packaging is an effective way to lower environmental impact without sacrificing quality. Designers are finding ways to use less plastic or other materials while keeping containers strong and functional. Even small reductions in weight can lead to significant decreases in carbon emissions during production and transport. This strategy not only supports sustainability goals but can also reduce costs related to materials and shipping. Thoughtful design helps balance the need for durability with the desire to minimize waste and carbon footprint.
7. Practical, Metallic, Textured, and Playful Look
The future packaging style sticks to simple, practical design ideas from mid-century influences. The shape tends to be blocky and geometric, creating a strong and straightforward look. Soft, muted colors like beige, grey, and off-white keep the design calm and easy on the eyes. Typography is simple and clear, often a single sans-serif font family to keep things neat. Rounded edges focus on being comfortable to handle rather than decorative, and matte finishes keep the surface from looking too shiny or flashy.
To bring in a modern edge, metallic finishes such as chrome, brushed steel, and polished aluminum are used. These surfaces reflect light and suggest strength. Typography here often shifts to condensed or monospaced fonts, which give a clean and engineered feel. The color scheme stays within cool greys and silvers but adds bright neon touches or metallic foils to attract attention subtly.
The packaging also shows signs of being handmade through textured surfaces. Techniques like stamping or embossing create slight imperfections, such as uneven ink or irregular shapes. The color palette includes earthy browns and greens, while typewriter-style or rough serif fonts add personality. Materials like recycled or uncoated paper support a raw, crafted look that feels more natural and genuine.
Unexpected shapes and playful designs complete this style by breaking traditional packaging norms. Products might be packed in containers shaped like unusual objects or made from surprising materials. These choices inject a bit of humor and curiosity into the design, encouraging shoppers to stop and explore.
Top 10 Product Packaging Design Trends 2026
How to make your packaging eye-catching? Start by understanding these product packaging design trends forecast for 2026.
1. Childish Design
This style brings a raw and imperfect quality inspired by children’s drawings. Packaging often shows uneven handwriting, playful doodles, shaky lines, and rough textures that look like crayons, markers, or pencils. Instead of aiming for slick and polished visuals, it highlights spontaneous and genuine marks. This design approach taps into emotions by offering a charming, vulnerable, and approachable look that feels refreshingly honest compared to precise, controlled designs.
2. Trinket Design
Packaging inspired by this trend looks like a carefully arranged collection or archive. Objects appear as isolated cutouts, placed symmetrically or floating on clean backgrounds. Sometimes, items are numbered or labeled like specimens in a catalog. The design treats each object with equal importance, no matter its size or function in reality. This style sparks curiosity and nostalgia by turning everyday things, like toys, keys, or vegetables, into collectibles, giving packaging a playful yet orderly feel.
3. Grainy Blur Design
The Grainy Blur Design trend features visuals filled with grainy textures, blurriness, and smooth gradients that create a rich, atmospheric effect. It includes several styles: large gradient fields that divide the design into simple, nostalgic sections with clean typography; soft, amorphous shapes resembling playful mascots painted with spray textures and bright neon colors; grainy, spray-painted gradients with fuzzy edges that give a handcrafted, imperfect feel, shifting between dreamy pastels and sharp neon hues; and soft, dissolving floral shapes rendered in pastel gradients that focus on mood and atmosphere rather than fine detail.
4. Type Collage
Typography takes center stage in this style, with letters layered, stretched, and overlapped in chaotic collages. Words become more of a visual texture than readable text. Packaging in this trend features distorted, cut, and warped letterforms combined with bold neon colors and high-contrast palettes. The design fills the surface with energy and attitude, often used for fashion or music products where emotional impact is more important than clarity.
5. Punk Grunge Design
Reviving the DIY spirit of the 1990s, this trend favors messy, rough, and unpolished packaging. Photocopy textures, graffiti scribbles, collage elements, and chaotic typography create a rebellious and urgent look. The color scheme mostly sticks to grayscale with splashes of neon. This style suits brands that want to feel authentic, countercultural, or streetwise, with raw analog marks that add personality to packaging.
6. Retro Pop Graphics
Bright, bold, and playful, this trend takes inspiration from the late ’80s and ’90s MTV graphics. Packaging often features exploding logos, cartoonish doodles, chunky 3D shapes, and loud neon colors. The designs celebrate randomness and fun, avoiding minimalism in favor of energetic visuals packed with abstract forms and electric colors.
7. Technical Blueprint
Packaging inspired by blueprints presents detailed line drawings, schematics, and annotations similar to architectural plans or patent documents. Objects break down into precise diagrams with numbered labels and grid layouts, usually set against classic blueprint blue or parchment backgrounds. This style communicates technical skill and craftsmanship, offering a clean yet detailed look that fits boutique or niche products well.
8. Warped Portraits
Human faces and bodies appear warped, stretched, or exaggerated in surreal and sometimes humorous ways. Packaging in this trend shows oversized heads, elongated limbs, and caricature-like features combined with bright, bold colors. The style mixes collage and cartoon elements, creating memorable and uncanny visuals. It fits fashion or entertainment brands that want a playful but striking identity.
9. Future Medieval Design
This style combines medieval sacred art with futuristic and digital textures. It features blackletter typefaces, illuminated borders, mythical creatures, and distressed parchment effects. Packaging creates a mood that feels ceremonial, mystical, or even apocalyptic by mixing ancient symbols with modern design touches. Brands wanting a visionary or fantasy-inspired look often turn to this style for storytelling through packaging.
10. Surveillance Tech
Inspired by security systems, this style uses elements like CCTV overlays, biometric scans, and infrared color schemes. Packaging looks raw and functional, with grids, timestamps, pixelated distortions, and machine-readable text. The aesthetic suggests exposure and vulnerability, often creating an uneasy but futuristic atmosphere. This trend fits brands that focus on technology, security, or experimental packaging concepts.