1. The Number of Molds
Several types of molds are typically used in the production of paper pulp products, including shape forming molds, hot pressing molds, reforming molds, and cutting molds.
-
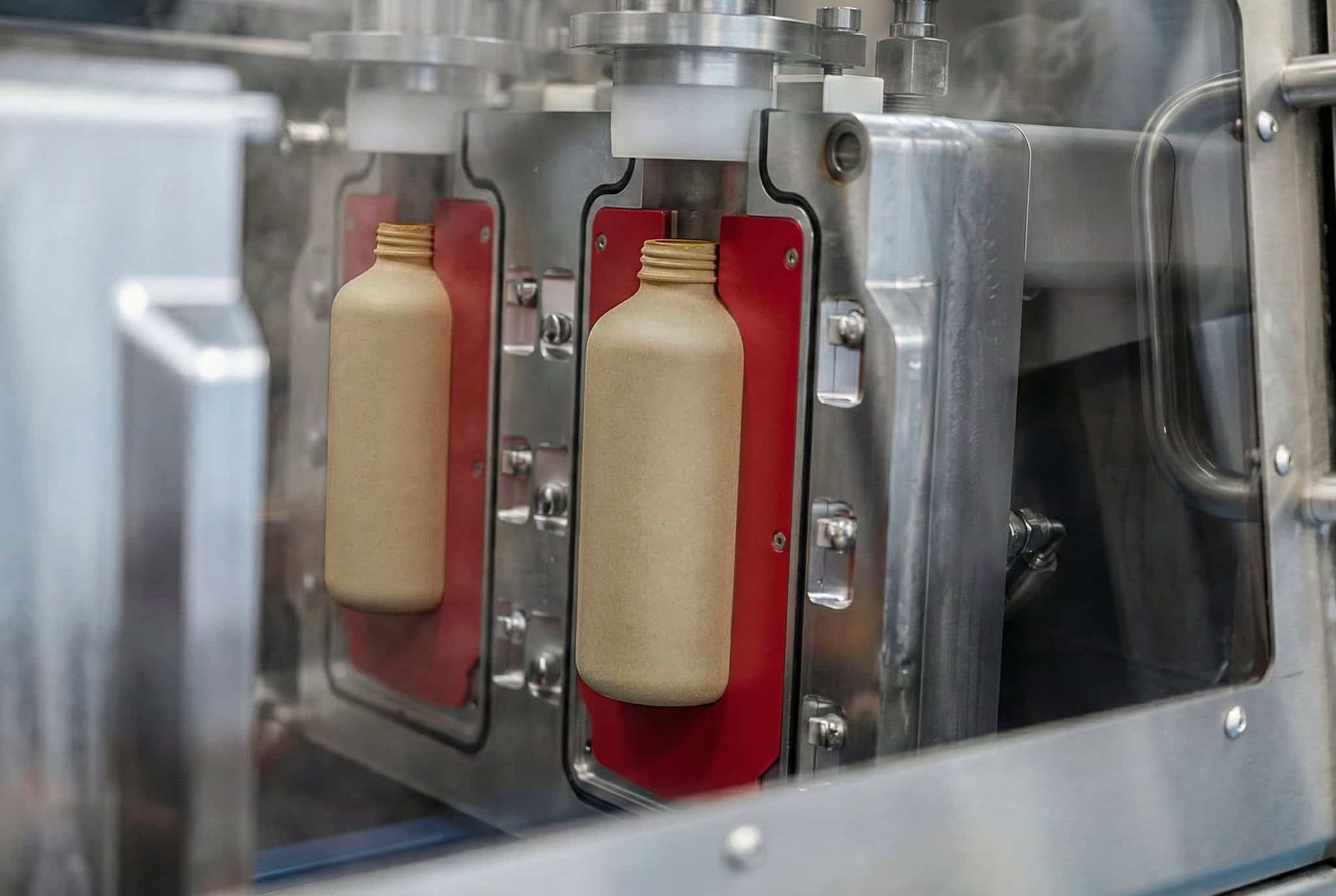
Shaped Forming Mold
In this mold, pulp material is transformed from a liquid or slurry state into a wet product with a defined shape during the initial shaping phase. During the molding process, this step sets the foundation for the product’s strength and structure.

-
Hot Pressing Mold
By using heat and pressure, a wet product is dried and finalized. As a result, the finished product has a smoother surface, better structural stability, and an overall better appearance.



2. Materials
Steel quality plays a direct role in the durability and performance of molds. A high-grade steel has superior wear resistance and heat tolerance compared to a lower-grade steel.
1) For example, steel rated for 1 million uses performs vastly better and lasts much longer than steel rated for 300,000 uses. The price of high-end steel can be over three times that of lower-quality alternatives.
2) A complete set of paper pulp molding can weigh several hundred kilograms, which means the raw materials will be expensive.

3. Number of Mold Cavities
Production efficiency and mold size are directly affected by the number of cavities in a mold.
1) It is possible to increase production capacity by increasing the number of cavities in a molding cycle.
2) However, additional cavities also mean a larger overall mold size, increased complexity, and higher manufacturing costs. The number of cavities should be carefully balanced with product size,equipment capacity, and production volume requirements.

4. Mold Fineness
High-precision molds require multiple processes of repeated machining and debugging to ensure dimensional accuracy, smooth edges, and clear texture definition of the final products.
1) Precision machining includes multiple engraving, grinding and polishing, as well as mold trial assembly and sampling.
2) The surface treatment process of molds also significantly impacts the appearance of finished products, particularly in the production of colored paper pulp and high-end product packaging.
5. Manual Process
Manual craftsmanship and technical expertise are required to produce molds.
1) This includes design and 3D modeling, CNC programming, precision assembly, and trial testing.
2) Each step demands skilled technicians to ensure the molds are precise, functional, and capable of producing high-quality, consistent output.

From Article: the original source